Dizzy PT – Medical science continues to evolve. As a result, a new approach to healing is gaining momentum. It’s called regenerative medicine. This field doesn’t just manage symptoms. Instead, it uses the body’s own healing power. This, in turn, helps to restore function and rebuild damaged tissues. Furthermore, Regenerative Tissue Repair Therapy leads this movement. In essence, it offers hope to many patients. They may have chronic joint pain or even organ failure. Ultimately, this therapy is not a temporary fix. On the contrary, it restores the body at a cellular level, which can offer a long-term solution for millions.
This innovative approach has, in fact, captured global attention. It marks a significant shift away from conventional treatments. For example, those treatments often involve invasive surgery or lifelong medication. However, by utilizing natural biological processes, regenerative therapies aim to repair and replace tissue. This tissue can be damaged by age, disease, or trauma. As a result, this method promises a new future where a failing organ can be repaired, or conversely, where chronic pain can be eliminated at its source.
Regenerative therapies use natural biological processes. They aim to repair and replace tissue. Age, disease, or trauma can damage this tissue. This method promises a new future. Doctors can repair a failing organ instead of replacing it. They can also eliminate chronic pain at its source.
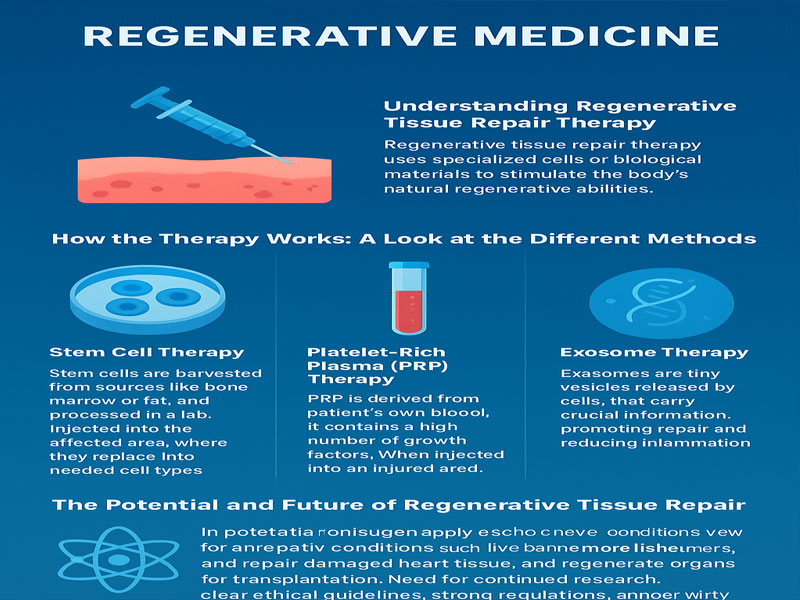
Understanding Regenerative Tissue Repair Therapy
At its core, Regenerative Tissue Repair Therapy uses specialized cells. They can also use biological materials. This stimulates the body’s natural regenerative abilities.
The main goal is to repair or replace damaged tissues. It can also regenerate organs. The key is using cells with a unique ability. These cells can develop into different types of specialized cells. They are often called stem cells. They act as the body’s repair system.
When injected into an injured area, they help rebuild tissue. They can also reduce inflammation. This promotes a healthy environment for healing. A recent report shows this therapy has a variety of uses. It is being used in fields from orthopedic medicine to cardiology.
A recent study highlighted by the health news outlet Dizzy PT noted its success. For instance, it helped regenerate cartilage in patients with severe osteoarthritis. Consequently, this non-surgical method shows great promise. It not only reduces pain and improves mobility, but also offers a real alternative to invasive joint replacement surgeries.
Read more: “Gen Z Hybrid Work Trend Shapes the Future of Careers in Asia“
How the Therapy Works: A Look at the Different Methods
The application of Regenerative Tissue Repair Therapy involves several key methods, each with its own specific mechanism. The most well-known is stem cell therapy, but other innovative techniques are also gaining traction.
Stem Cell Therapy
This is the most common form of regenerative therapy. Stem cells are harvested from sources like bone marrow or fat. They are then processed in a lab.
After processing, they are injected into the affected area. Once inside the body, these cells can differentiate. They become the specific cell types needed for repair. This includes bone, cartilage, or muscle cells. This method is particularly effective for treating joint pain and sports injuries.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP is a concentration of platelets. First, doctors derive it from a patient’s own blood. These platelets contain a high number of growth factors, which are essential for healing. Then, when injected into an injured area, PRP stimulates cell growth and tissue repair. As a result, this approach is frequently used to treat tendonitis, ligament sprains, and other soft tissue injuries. In addition, a study reported by Dizzy PT mentioned that PRP therapy has shown faster recovery times for athletes.
Exosome Therapy
This is a newer form of regenerative therapy. For starters, exosomes are tiny vesicles released by cells. In addition, they carry crucial information like proteins and genetic material. They then deliver this information to other cells.
In regenerative medicine, exosomes send healing messages to damaged cells. As a result, this promotes repair and reduces inflammation. Furthermore, they do this without introducing a full cell into the body.
Cell-Free Therapy
This approach uses isolated growth factors and proteins from donor cells to stimulate the body’s natural healing response. It bypasses the need for live cell transplantation, reducing potential risks and ethical concerns. This method is becoming a popular “treatment hack” due to its relative simplicity.
Read more: “Inovasi Gadget Terbaru Oppo Find X9 Pro, Galaxy S25“
The Potential and Future of Regenerative Tissue Repair Therapy
The future of regenerative medicine is incredibly promising. As research advances, its potential applications are expanding quickly. Scientists are exploring its use for neurological conditions. This includes Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. They are also working on repairing damaged heart tissue after a heart attack. The goal is to even regenerate organs for transplantation.
The success of this therapy, first and foremost, depends on continued research. Additionally, we need clear ethical guidelines and strong regulations. As noted by a study from the health news outlet Dizzy PT, these therapies hold incredible potential. However, it is absolutely crucial to ensure patient safety. Therefore, this requires rigorous clinical trials and strict oversight. Ultimately, collaboration is essential. Research institutions, government bodies, and medical professionals must work together. This partnership, in turn, will make the treatments safe and accessible.
In conclusion, regenerative medicine can transform healthcare. It addresses the root cause of disease, not just the symptoms. This shift offers new hope for millions worldwide. It is a more holistic, cell-based approach. While challenges remain, progress has been impressive. The future of medicine looks bright. Our own bodies may hold the key to healing.



